Whether you’re a runner pounding the pavement or just climbing stairs to your apartment, your knee plays a pivotal role in how you move through the world. But how often do we really think about this complex joint until something goes wrong?
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of knees—examining their structure, common conditions, treatments, and proactive ways to protect them. Whether you’re dealing with knee pain or simply want to keep your knees strong and healthy, we’ve got you covered
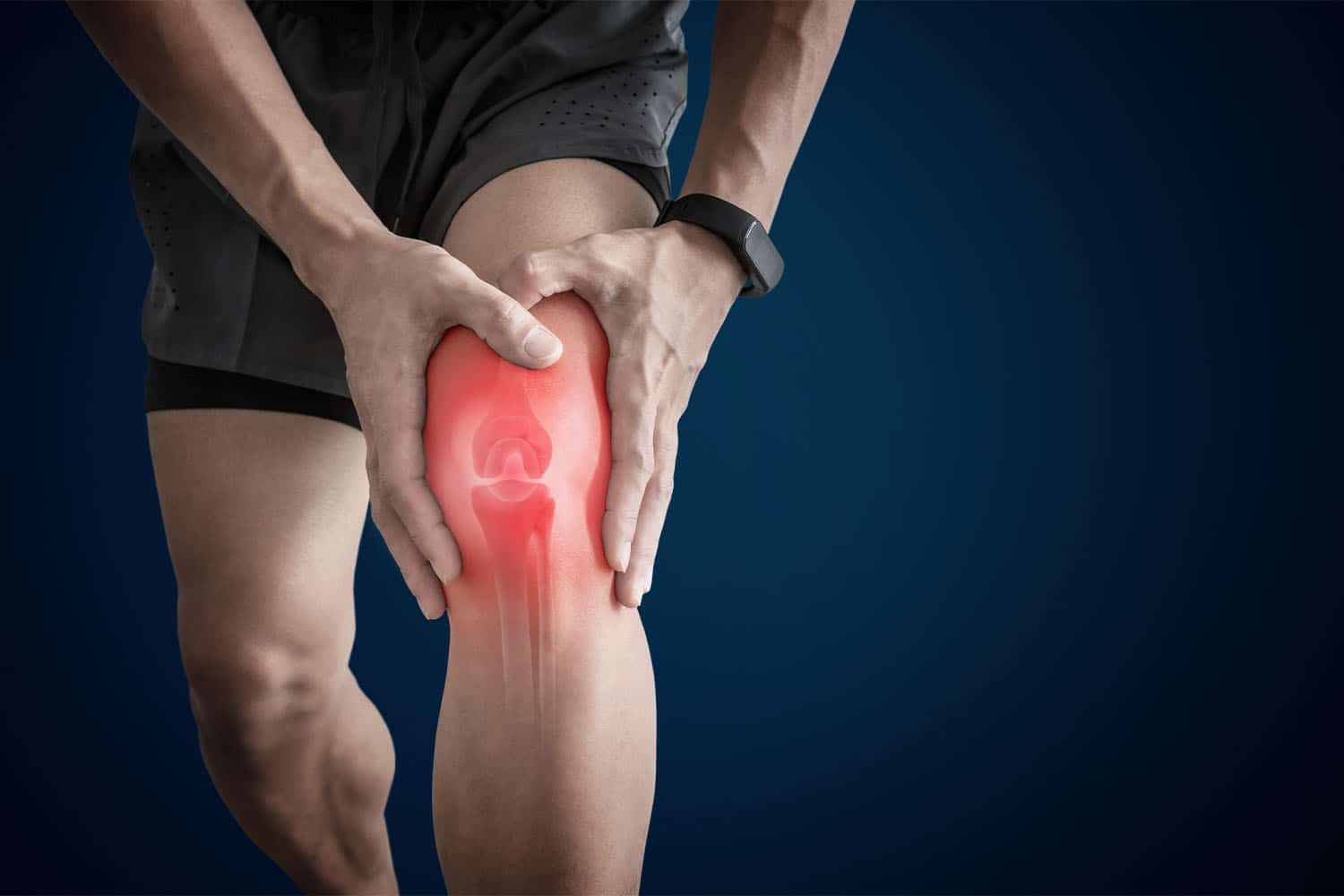
Understanding Knee Anatomy
Your knee is more than just a hinge. It’s a sophisticated engineering marvel that absorbs shock, provides stability, and supports your body weight. Here’s what makes up the knee:
Hinge of Complexity: The Main Components
- Bones: The knee connects three bones: the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and patella (kneecap).
- Cartilage: Two types of cartilage—articular cartilage and the meniscus—provide cushioning and allow smooth movement.
- Ligaments: ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL keep your knee stable.
- Tendons: These connect muscles to bones and facilitate movement.
Common Knee Injuries and Conditions
Ouch! Why Does My Knee Hurt?
Knee issues range from minor annoyances to major impairments. Here are some usual suspects:
1. ACL Tears
Common in athletes, this injury often requires surgery and extensive rehab.
2. Meniscus Tears
These occur when you twist your knee while bearing weight. Think: sudden squat with a twist. Yep, not fun.
3. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Also known as “runner’s knee,” this condition causes pain at the front of the knee.
4. Osteoarthritis
The wear-and-tear villain. This degenerative joint disease affects millions, especially as we age.
5. Bursitis
Inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction in the joint.
Causes of Knee Pain
Knee pain doesn’t always come from injury. Sometimes, it’s your lifestyle whispering (or shouting) that change is needed.
Risk Factors
- Age: Cartilage wears down over time.
- Weight: Extra pounds add stress.
- Overuse: Repetitive motion without rest? The knee says no.
- Improper Technique: In sports or exercise, form matters—a lot.
Diagnosis: What To Expect
If your knee is giving you grief, here’s what to expect at the doctor:
Medical History and Physical Exam
They’ll ask about symptoms and may move your leg to check for range of motion and pain triggers.
Imaging Tests
- X-rays to check bones.
- MRI for soft tissues like ligaments and cartilage.
- CT scans for detailed bone images.
Treatment Options
Conservative Treatments
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE)
- Physical therapy to strengthen muscles around the knee
- Medications like NSAIDs for pain relief
Invasive Treatments
- Injections: Corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid for inflammation or lubrication
- Surgery: Arthroscopy, partial or total knee replacement depending on severity
Preventing Knee Injuries
An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of knee braces.
Tips to Keep Knees Healthy
- Strengthen your muscles, especially quads and hamstrings.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint stress.
- Stretch and warm up before activity.
- Wear proper shoes with good support.
- Use correct technique during exercise or sports.
Real-World Advice: Staying Active with Knee Concerns
Let’s get real: knee issues don’t mean the end of your active life. It just means playing smarter.
Smart Activities for Troubled Knees
- Swimming or water aerobics
- Cycling
- Walking on soft surfaces
- Strength training (focus on form!)
When to See a Specialist
Don’t tough it out if you experience:
- Persistent swelling
- Inability to fully extend or bend your knee
- Obvious deformity
- Popping or grinding sounds with pain
Better safe than sorry—early intervention can save you from long-term damage.
When to See a Specialist
Don’t tough it out if you experience:
- Persistent swelling
- Inability to fully extend or bend your knee
- Obvious deformity
- Popping or grinding sounds with pain
Better safe than sorry—early intervention can save you from long-term damage.
